OVERVIEW
FEMALE HAIR LOSS
Mistakenly thought of as a male disease, around 40% percent of women will suffer from some form of hair loss by the age of 50. A woman’s hair is an important part of her aesthetic make-up. It represents her style and taste, and frames her face while accentuating her best features. Unfortunately, most physicians don’t have answers or solutions for women who begin to lose their hair. Plano, TX hair restoration surgeon, Dr. Joseph Yaker, understands that this can be extremely catastrophic to a woman’s self-confidence, body image and quality of life. Clinical studies have shown that psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety are more common in people with hair loss, especially women.
TYPES OF FEMALE HAIR LOSS
Around 30 million U.S. women will experience hereditary hair loss, or female pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia), while others will struggle with situational hair loss, brought on by medical conditions, medications, poor health and nutrition, environmental factors such as smoking and sun damage, or even from adverse reactions to hair care products or treatments.
FEMALE ANDROGENETIC ALOPECIA
It is perfectly normal for people to shed 50 to 100 hairs per day. This generally doesn’t cause noticeable thinning of scalp hair because new hair is growing in at the same time that hair is shedding. However, hair loss occurs when this hair growth cycle and shedding is disrupted or when the hair follicle becomes destroyed and replaced with scar tissue. Female pattern hair loss (androgenetic alopecia) is the most common form of hair loss in women. This occurs gradually and is caused by genetics (from either side of the family), age, and the action of a specific male hormone, dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This hormone is found in lesser amounts in women and it preys on the hair follicles, preventing them from receiving vital nutrients for proper hair follicle growth, leading to the hairs shrinking, and resulting in a shorter lifespan. Interestingly, DHT does not need to be elevated to generate hair loss. Estrogen, when lowered as commonly seen in menopause, creates a change in the ratio of male to female hormones, giving an edge to these male hormones. Compounded with the sensitivity of DHT to the hair follicles, heredity can affect the age at which a woman begins to lose her hair, as well as the rate of hair loss and the extent of baldness.
TELOGEN EFFLUVIUM
Telogen effluvium is the second most common type of hair loss. It is predominantly seen in women between the ages of 40-70, but may occur at any age. Its symptoms include excessive thinning, shedding, and balding and it may happen abruptly. Common causes of sudden hair loss include changes in hormone levels such as with child birth, menopause, poor nutrition, medical conditions such as iron deficiency anemia and hypothyroidism, medications, severe illness or infection, major surgery, and even extreme levels of stress.
Female Hair Loss Treatment
The complex actions of genetics, DHT, shifting of hormone ratios and age-related volume loss can commonly occur in women in their 40’s and 50’s. However, just like in men, genetic hair loss can appear at all ages after puberty. In fact, hair loss occurs with relatively high frequency even in women in their 20’s and 30’s. The majority of women with female pattern hair loss initially develop diffuse thinning over the front and top of the scalp, while maintaining the frontal hairline. This thinning may present with a widening through the central part line while others may present initially with either episodic or continuous hair shedding, prior to any noticeable decrease in hair volume. In addition, thinning may also be seen throughout the scalp, including the temple areas as well as the back and sides.
FEMALE HAIR LOSS PATTERN
Female pattern hair loss has several different patterns and are described based on different scales.
LUDWIG SCALE
This is the most common classification for female pattern hair loss. There are 3 stages (ranging from mild hair loss to extensive, severe widespread thinning) and in each stage hair loss occurs on the front and top of the scalp with relative preservation of the frontal hairline. Regardless of the extent of hair loss, only women with stable hair on the back and sides of the scalp are candidates for hair transplant surgery.
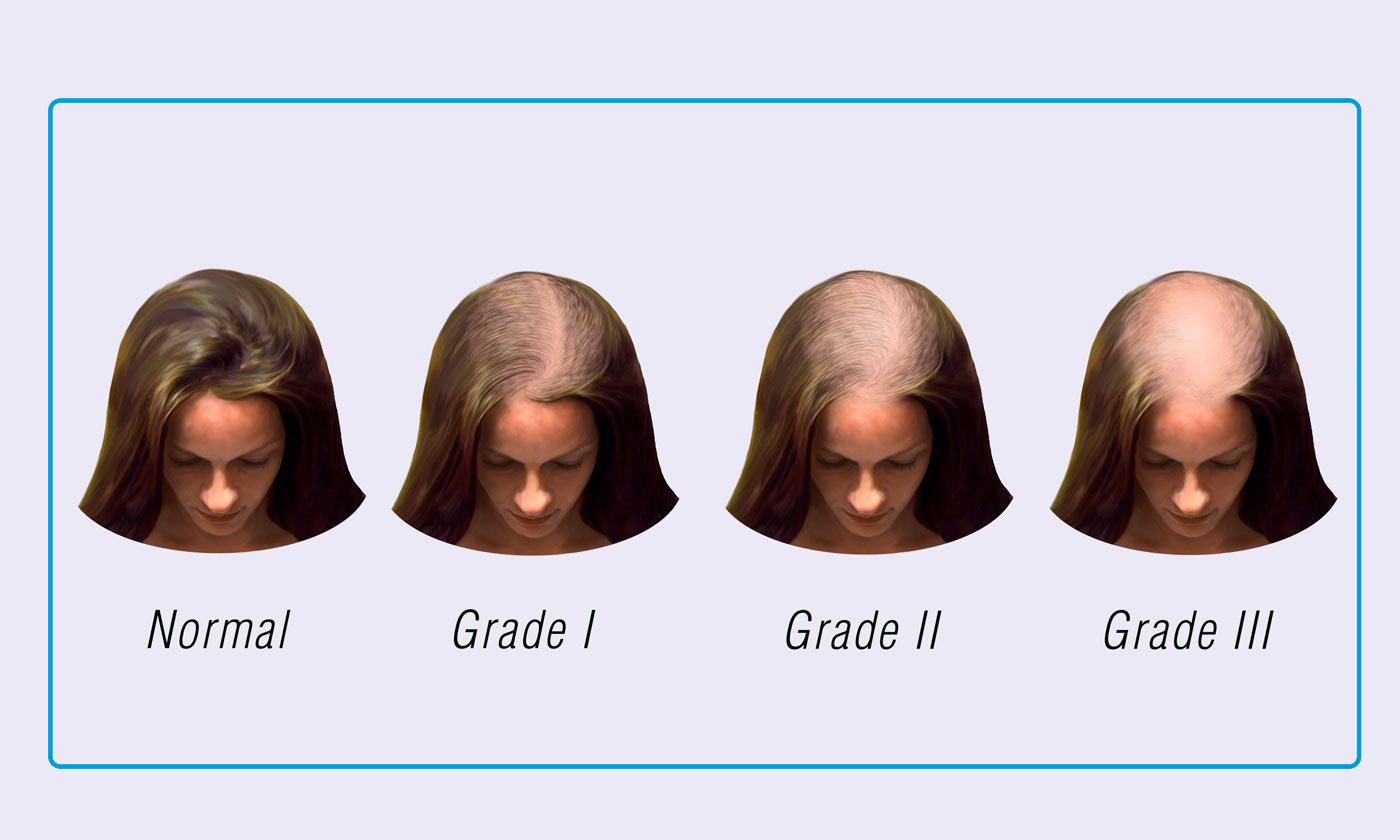
SINCLAIR SCALE
For many men and women, their hair loss is due to androgenetic alopecia (male and female pattern baldness), and is driven by three factors – genetics, androgens (male hormones), and age. Genetic hair loss can come from either side of your family and can skip a generation. Hereditary hair loss is quite common, affecting about 50 million men and 30 million women in the U.S. alone.
NORWOOD SCALE
This scale represents frontal and crown hair loss and is associated with bitemporal recession (which is similar to male pattern baldness). This is not common among women and usually presents itself with thinning or recession to the temples and the crown area.
OLSEN SCALE
This pattern of hair loss represents a “Christmas Tree”, as the hair thinning is wider in the front part of the scalp giving the thinning area a triangular-shaped figure.
DIAGNOSIS OF FEMALE HAIR LOSS
Hair loss in women isn’t always as straightforward as it is in most men. In men, about 95 percent of all cases are caused by male pattern baldness. In women, however, hair loss can be triggered by a multitude of conditions and circumstances. During the consultation, Dr. Yaker utilizes specialized hair and scalp scanning technology to assess the distribution of hair loss, hair thickness, and how much hair is present in a particular area. It is important to note, that for women, a proper diagnosis begins with a process of elimination. More than one cause for the hair loss may coexist and need to be recognized or excluded. A comprehensive medical history, which includes a list of all medications, history of hair loss, a thorough scalp exam, a discussion of medical and skin disorders, and a complete nutritional evaluation will be needed. Blood work analysis may be required, and a scalp biopsy may also be performed if the cause of hair loss is uncertain or there is a concern for scarring alopecia.
FEMALE HAIR LOSS TREATMENTS
While female hair loss may not cause physical pain, it does cause mental anguish. Fortunately, in many cases, female hair loss can be successfully treated with today’s advanced nonsurgical and surgical treatment options. After a diagnosis has been confirmed, Dr. Yaker will create a Customized Treatment Plan depending on one’s hair characteristics, the level of hair loss and the aesthetic goals of the patient.
NONSURGICAL TREATMENTS
There are numerous nonsurgical treatments that when combined, can offer significant hair improvements. Dr. Yaker’s Volumizing Glycolic Acid Shampoo and Conditioner help restore vitality to the hair by deep cleaning the scalp and reestablishing lost moisture content and physiological pH to the scalp and hair. Dr. Yaker has also formulated his own oral supplement, which is a blend of Aminoplex hair repair vitamins. This is made up of amino acids (building blocks of protein) that produce keratin, which makes up close to 97% of our hair. In addition, Dr. Yaker’s specially compounded FDA approved topical medication, Minoxidil (brand name: Rogaine®), is clinically proven to help slow down, stop and even reverse hair loss in women. Other nonsurgical therapies offered are Low Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) using the advanced LaserCap®, and Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) with placenta-derived extracellular matrix therapy to help restore thinning hair. Lastly, Dr. Yaker offers scalp and facial micropigmentation where permanent ink is applied to the skin, creating micro dots that replicate the natural appearance of hair. This is used for the scalp and eyebrows.
HAIR TRANSPLANT SURGERY
For some patients, nonsurgical hair restoration methods may not be enough to restores one’s hair loss or a patient may present with advanced loss. Depending on the cause of hair loss, hair transplantation surgery may be the best approach to restore one’s confidence and quality of life by restoring hair through extremely advanced techniques.
According to the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery, since 2004, the number of female surgical hair restoration patients worldwide increased 24 percent. Modern surgical hair restoration procedures such as Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) allow surgeons to take hair from the back of the head (genetically permanent hair zone) and transplant it to the areas where balding has occurred. The reason why the hair does not fall out once transplanted in its new location is because those hair follicles take on the same characteristics as the hair in the area where it originated, the genetically permanent zone. Both approaches result in lasting outcomes. In order to know if you are a candidate, Dr. Yaker will go over your medical history and examine your hair and scalp. He will determine if you have ample, good quality hair in the permanent hair zone in order to be able to relocate those hair follicles to the areas of hair loss.
GET IN CONTACT
If you are suffering from slow or rapid hair loss and your hair thinning is becoming noticeable, or if you have balding that you wish to cover with new hair growth, we invite you to call our hair restoration practice today. Plano, TX hair transplant surgeon, Dr. Joseph Yaker will provide a comprehensive medical and hair loss history, and scalp and hair analysis that will allow him to provide each patient with an accurate diagnosis so that a patient-specific treatment plan can be put into action.
